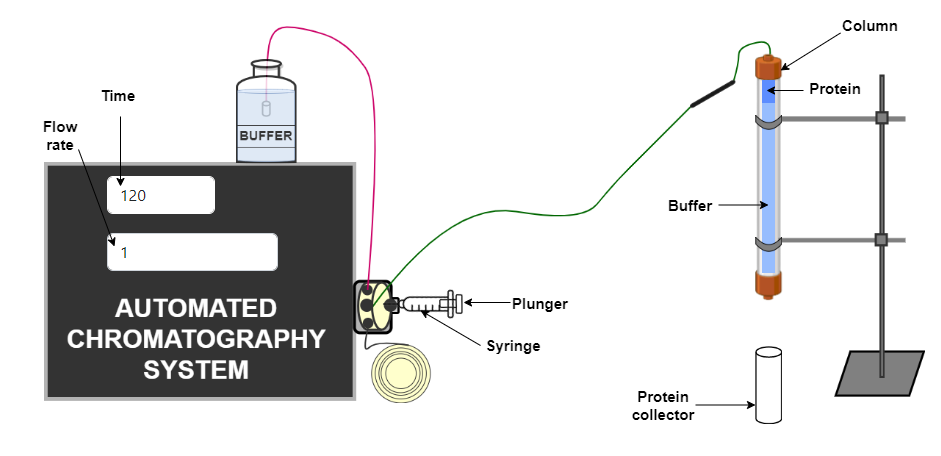
Procedure
In order to perform a size exclusion chromatography, the following steps must be followed:-
- Chromatography media selection: The media must be chosen on the basis of the aim of the experiment (high-resolution fractionation or group separation ) and the molecular weights of the target proteins and contaminants to be separated. Superdex media is the primary choice for high resolution, short run times, and high recovery. Sephacryl is used for fast, high-recovery separations at laboratory and industrial scales. Superose offers a broad fractionation range but is not suitable for large-scale or industrial-scale separations. Sephadex is preferred for rapid group separations such as desalting and buffer exchange.
- Buffer composition and equilibration of the column: Running Buffer composition does not affect the resolution obtained in size exclusion chromatography since the separation occurs on the basis of different size of the biomolecules. The most important thing to be considered is the effect of buffer composition on the shape or biological activity of the molecules of interest. Buffer must be selected with a suitable pH and salt composition that are compatible with protein stability and activity and in which the product of interest should be collected. 0.15 M of NaCl must be included in the buffer to avoid non-specific ionic interactions with the matrix (shown by delays in peak elution). Buffer solutions must be filtered and degassed before use , as air bubbles can significantly affect performance. The column matrix must be equilibrated with one column volume of buffer before use.
- Protein sample preparation: Sample preparation is an essential step for size exclusion chromatography. Correct sample preparation reduces the risk of unnecessary blockage of the column and stringent washing procedures and helps in extending the lifetime of the column. The sample must be clear and free from particulate matter, bubbles, and precipitate and must be centrifuged and filtered with a 0.22 µm filter before injection in the column. We must not use sample concentration above 70 mg/ml as high viscosity of the sample may interfere with the separation.
Figure 1 : Sample containing mixture of protein
- Sample injection and fraction collection : Samples can be applied directly to the column via a chromatography system, a peristaltic pump, or a syringe.
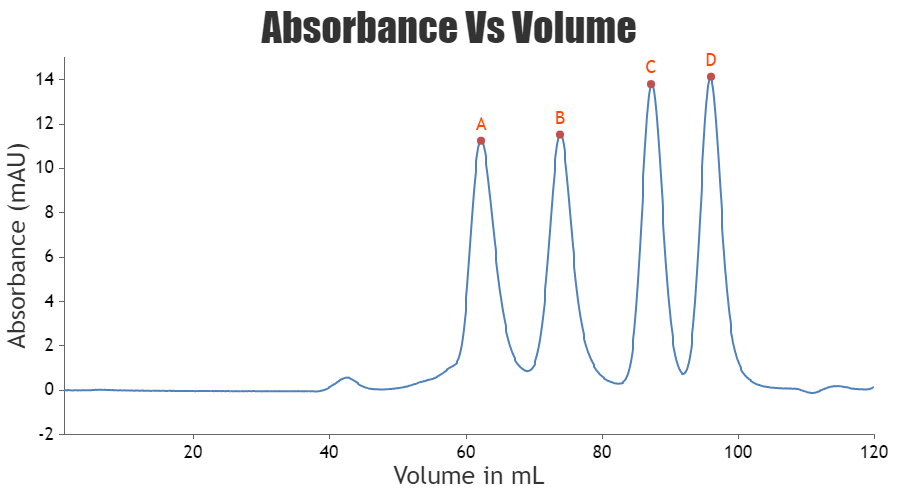
Samples are then eluted isocratically using a single buffer on the basis of their decreasing molecular weight. After sample injection, the entire separation takes place as one column volume of buffer (equivalent to the volume of the packed bed) passes through the column and the separate fractions containing the different-sized proteins are collected. Maximum resolution is obtained with a long column and a low flow rate.
- Data acquisition:
- SDS PAGE analysis : The eluted protein fractions can be further analyzed using SDS PAGE.
- Care of size exclusion chromatography medium: When a size exclusion chromatography medium has been in use for some time, it is necessary to remove precipitated proteins or other contaminants. We need to clean the column when there is an appearance of a coloured band at the top of the column, a space between the upper adaptor and the bed surface, a loss in resolution of protein peaks, or a significant increase in back pressure in the column. Cleaning with filtered NaOH (0.5M-1M) is highly efficient, prolongs column life, and minimizes the risk of contamination between runs