



pH-titration of amino acids and small peptides, and estimation of isoelectric point (pI)
Simulation instruction
pI calculation instruction
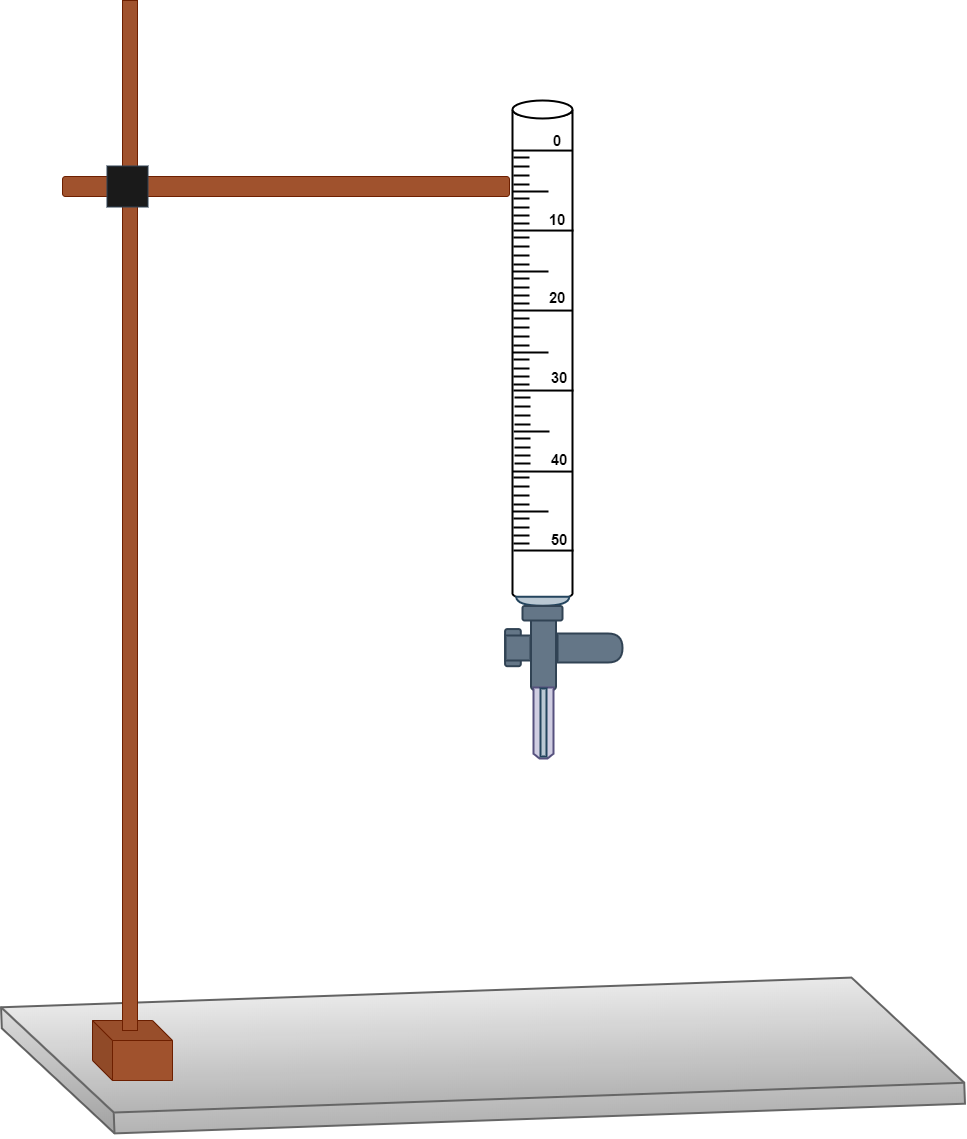
| Step 1 | The pH of the amino acid solution is lowered using 0.1 M HCl. Then, 0.1 M NaOH is used for titration of the chosen amino acid to determine its isoelectric point. |
| Step 2 |
|
| Step 3 |
|
| Step 4 | |
| Step 5 | |
| Step 6 |
|



| Amino Acid | Side Chain | pKa1 (α- COOH) |
pKa2
(α-NH3 +) |
pKR (R-group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine (G) | H | 2.34 | 9.60 | - |
| Alanine (A) | CH3 | 2.34 | 9.69 | --- |
| Valine (V) | (CH3)2CH | 2.32 | 9.62 | --- |
| Leucine (L) | (CH3)2CHCH2 | 2.36 | 9.60 | --- |
| Isoleucine (I) | CH3CH2CH(CH3) | 2.36 | 9.68 | --- |
| Serine (S) | CH2OH | 2.21 | 9.15 | --- |
| Threonine (T) | CH(OH)CH3 | 2.09 | 9.10 | --- |
| Cysteine (C) | SH | 1.96 | 8.18 | --- |
| Methionine (M) | SCH3 | 2.28 | 9.21 | --- |
| Proline (P) | Fused to α-N | 1.99 | 10.60 | --- |
| Phenylalanine (F) | C6H5 | 1.83 | 9.13 | --- |
| Tyrosine (Y) | C6H4OH | 2.20 | 9.11 | 10.07 |
| Tryptophan (W) | C8H6NCH2 | 2.38 | 9.39 | --- |
| Histidine (H) | C5H4NCH | 1.82 | 9.17 | 6.00 |
| Asparagine (N) | CH2CONH2 | 2.02 | 8.80 | --- |
| Glutamine (Q) | CH2CONH2 | 2.17 | 9.13 | --- |
| Glutamic acid (E) | CH2CH2COOH | 2.19 | 9.67 | 4.25 |
| Aspartic acid (D) | CH2COOH | 1.88 | 9.60 | 3.65 |
| Lysine (K) | CH2CH2CH2NH3+ | 2.18 | 8.95 | 10.53 |
| Arginine (R) | C4H6N3+(NH)2 | 2.17 | 9.04 | 12.48 |

| pH | 1 | 2.5 | 7 | 10 | 13 |
| Net Charge |