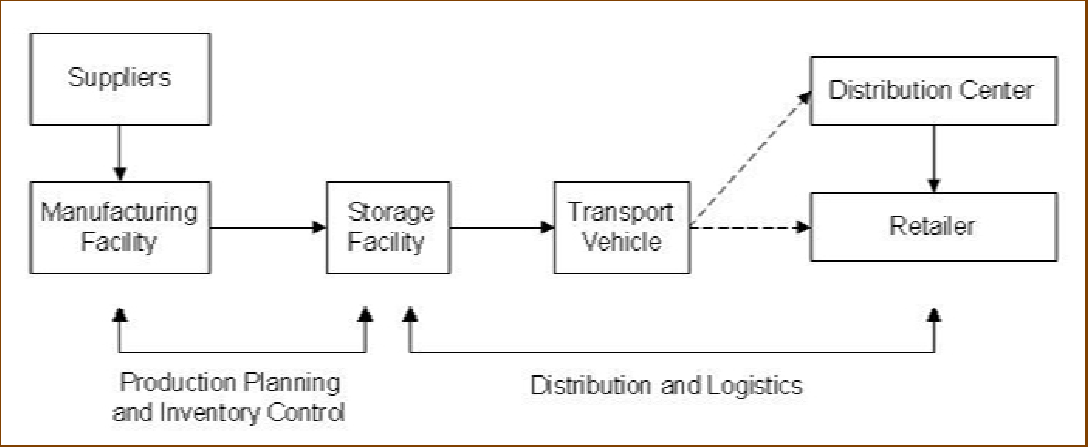
Supply chain is an integrated manufacturing process wherein raw materials are converted into final products, then delivered to customers.At its highest level, a supply chain is comprised of two basic, integrated processes:
(1) The Production Planning and Inventory Control Process, and
(2) The Distribution and Logistics Process.
In the Soft Drinks game students enact a four stage supply chain (Retailer, Wholesaler, Distributor, and Manufacturer). The task is to produce and deliver units of soft drinks: the factory produces and the other three stages deliver the beer units until it reaches the customer at the downstream end of the chain
The aim of the players is rather simple: each of the four groups has to fulfill incoming orders of soft drinks by placing orders with the next upstream party. Communication and collaboration are not allowed between supply chain stages, so players invariably create the so called bullwhip effect.
1. The task of each supply chain is to produce and deliver units of soft drinks: the factory produces and the other three stages deliver the beer units until it reaches the external customer at the downstream end of the supply chain.
2. The game is played in rounds, which simulates weeks.
3. Player has to decide on the amount to be ordered in each round.
4. Deciding on each round’s order amount is effectively the only decision that players are able to make throughout the game.
1. Every order has to be fulfilled, either directly (should the players' inventory be large enough) or later in subsequent rounds.
2. Inventory and backlog incur cost - each item in stock costs Rs 1 per week, while each item on backlog costs Rs. 2. Consequently, the primary aim of is to keep their costs low.
3. Hence, the optimal strategy for the players is to run their business with as little stock as possible without being forced to "move into backorder".
4. Players are not allowed to communicate. The only information they are allowed to exchange is the order amount; there is no transparency as to what stock levels or actual customer demand is; only the retailer knows the external demand.
5. The external demand is predetermined and usually does not vary greatly.
6. In the beginning, the supply chain is pre-initialized with inventory levels (e.g. 12 units), orders (e.g. 4 units) and soft drinks units in the shipping delay fields (e.g. 12 units), Lead Time (3weeks). Hence three orders each of 4 units is in delay.
7. In order to induce the bullwhip effect, the external demand remains stable for a few rounds (e.g. 4 units for 2 rounds) before it suddenly shows one steep increase (jumps to 8 units) before it remains stable again at this higher level for the remainder of the game (usually 20 to 30 rounds in total).
8. The one increase in external demand inevitably leads to the creation of the bullwhip effect and to a destabilization of ordering patterns throughout the supply chain.