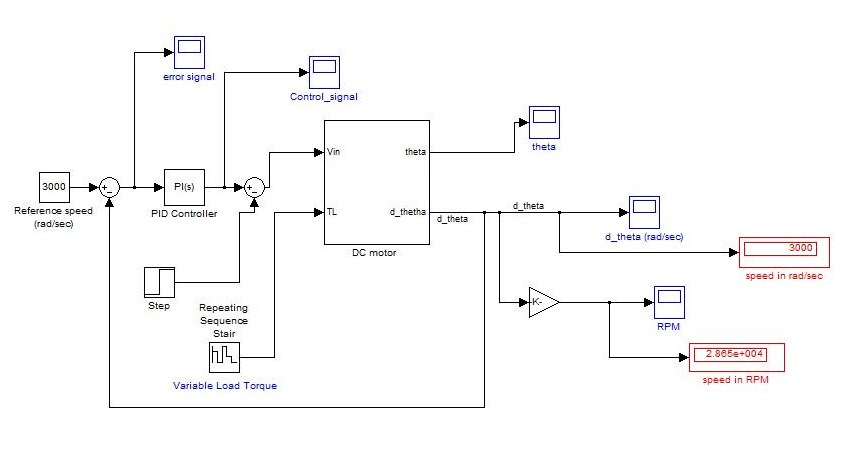
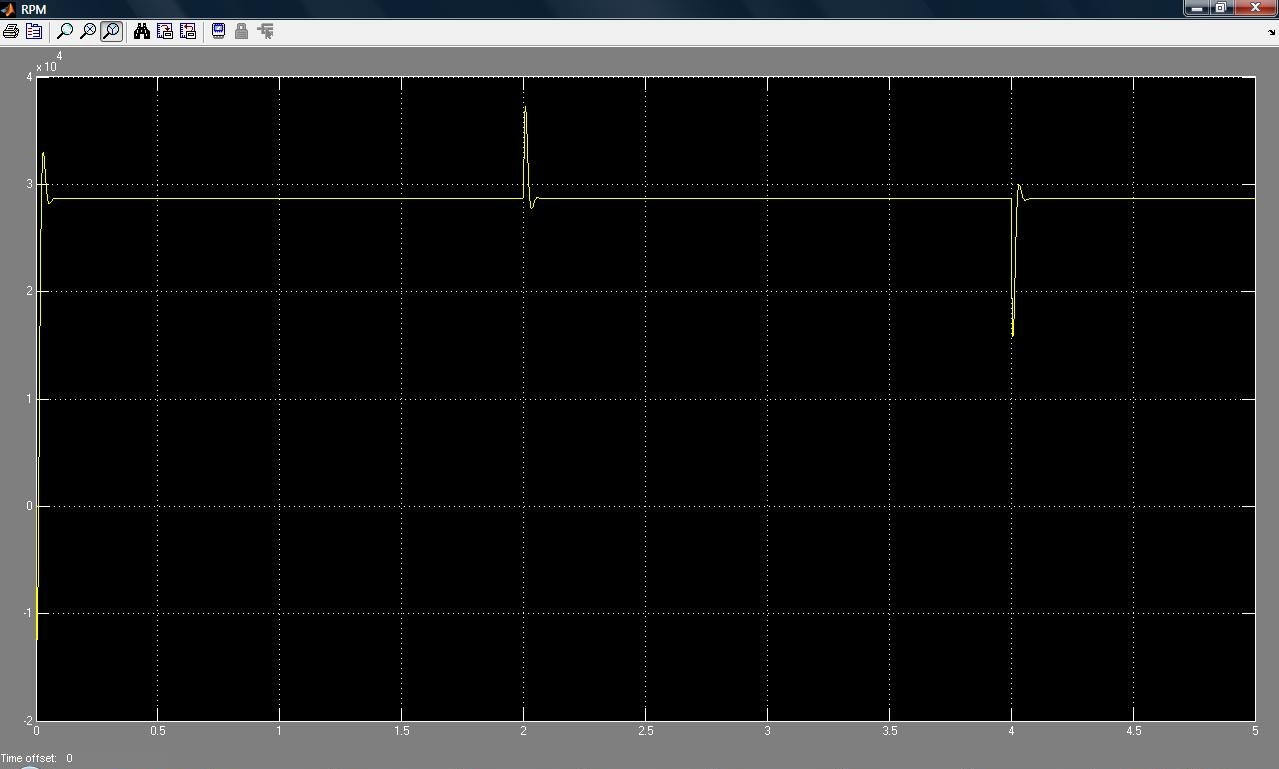
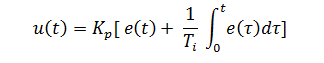CLOSED LOOP CHARACTERISTICS OF DC MOTOR
PROPORTIONAL AND INTEGRAL CONTROL
PI Controller (proportional-integral controller) is a feedback controller which drives the plant to be controlled
with a weighted sum of the error (difference between the output and desired set-point) and the integral of that value.
It is a special case of the common PID controller in which the derivative (D) of the error is not used.
The controller output for PI controller is given by:
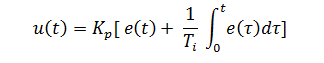
Where
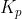
is the Proportional control gain and
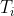
is the integral time.
Advantages and disadvantages:
- The integral term in a PI controller causes the steady-state error to reduce to zero, which is not the case for
proportional-only control in general.
- The lack of derivative action may make the system more steady in the steady state in the case of noisy data. This is
because derivative action is more sensitive to higher-frequency terms in the inputs.
- Without derivative action, a PI-controlled system is less responsive to real (non-noise) and relatively fast alterations
in state and so the system will be slower to reach set-point and slower to respond to perturbations than a well-tuned
PID system may be.